Pumpkins are creeping and climbing plants with an annual cycle. There are wild versions in their countries of origin and, of course, on all continents, cultivated.
In our latitude, the seeds are usually planted at the beginning of spring. In the first weeks, we must make sure that the seedbed remains moist. After two or three weeks, they are usually replanted in fertilized soil, in small trenches about 30 centimeters deep.
They take advantage of the sunny days to increase during May, spreading through the ground with stems and branches that grow for days. We will continue to water them frequently but avoid flooding them. The leaves are large, covered by a light fluff of fine hair. Its flowers appear early, yellowish or orange, trumpet-shaped like those of zucchini.
We recommend consuming them during the fall and winter. But it must be said that the development of the intensive agricultural industry, with the control of temperatures and humidity, allows today to extend its cultivation for a good part of the year. In addition, if they are kept with their peduncle, or small stem, intact, in dry, dark warehouses, with mild and ventilated temperatures, they can be kept in good condition for many months. Once opened, they must be kept in the refrigerator and consumed in the following days.
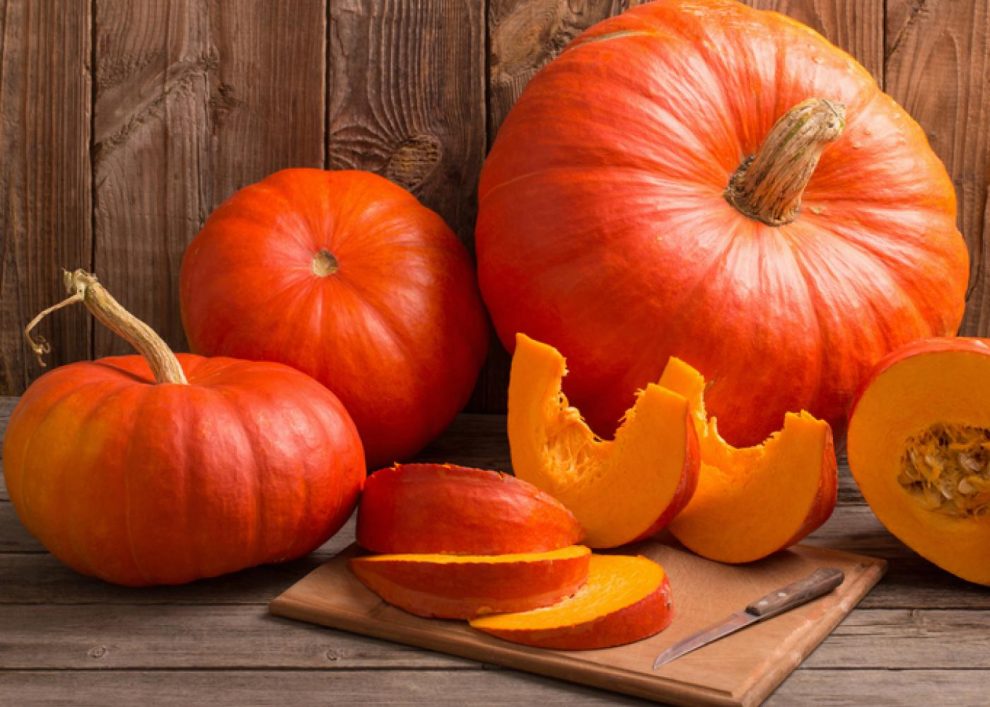
The fruits or berries can be varied according to the subspecies; we know them round or elongated, especially with their characteristic rounded cello shape. There are medium and enormous sizes. As a curiosity, there are agricultural contests to reward the largest ones. In 2016 a Belgian farmer, M. Willemijns, won a contest with a 1,190-kilogram specimen, more than a ton in weight, enough to feed a regiment!
Pumpkins are also distinguished by the texture and color of their rind, which is usually very hard, sometimes smooth, and sometimes rough. There are pale, cream, yellowish, orange, and even green tones.
Pumpkin production
According to data from the European Community, Spain is the leading European producer of pumpkins, with 115,000 tons in 2017, ahead of France and Germany. Local production has exploded due to high international demand, doubling in less than ten years. Indeed, a large part of the collection is dedicated to export in the EU, precisely to France, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, or Germany.
Our geography is in the Valencian Community and Andalusia, where most of this berry is grown.
Pumpkin varieties
The great geographical diversity of its cultivation means that there are a large number of varieties; let’s review some of the best known:
Fiddle or peanut squash. The most popular in Spain. It is widely used in our cuisine for its thin skin and dense and tasty pulp, with a mild flavor, not excessively sweet. Its shape is the characteristic rounded violin shape. Its light external color, compared to the pulp that has an intense orange.
La Vasca or Mallorca. Similar to the previous one, but with a more elongated shape. The skin also varied, with a dark green tone and streaked with lighter stripes.
Pilgrim's gourd or Sinatra. It is also called white Valencian pumpkin, precisely one of the regions with the highest consumption of pumpkin. In this case, the pulp is whitish and tender, reminiscent of zucchini.
Cucurbita maximum. It is easy to describe because we mean the typical Halloween pumpkin. They are of various sizes, some very large, with round and flat shapes. Its shell is hard and rough, with grooves that run from the base to the upper end.
Totanera or Murcian squash. The most unique is their thick, dark green bark, and they also have small irregular warts. The shape is rounded and flat. The pulp, on the other hand, is intense orange or yellowish. The most common use is as an ingredient in stews and soups.
Spaghetti type or spirals. Both the skin and the interior are light cream. Its name derives from its stringy and fibrous pulp. Therefore, they are not suitable for handling with cream or puree. They are cooked in halves or whole.
Confectioner or Citron. It is a delightful pumpkin whose use is dedicated to making angel hair. It is a broad specimen with stringy and juicy flesh.Main types of pumpkin on the market
The arrival of traditional pumpkins from other countries and the development of new varieties, and the recovery of local products make it difficult to establish a complete list of all the types of pumpkin that we can find today in stores. The diversity of names and nicknames makes the task more complicated, but we can list a number of the most common generic varieties.
Pumpkins1
Butternut, peanut, or violin. It is the most cultivated in Spain and has been believed the most in this epoch. Called squash in English, thus clearly differentiating itself from the typical Halloween pumpkin, the peanut pumpkin is elongated, with light and smooth skin, a broader base, and bright orange pulp. It is one of the most versatile and grateful for cooking, with the thin skin and brown pulp, which are firm and tasty without being excessively sweet.
Potimarrón or Hokkaido. It is more rounded and flattened, with fruits that do not usually exceed a kilo and a half in weight, although it can grow much more if left to its own devices. The skin is more demanding, more intense orange, and furrowed with parallel vertical lines of a lighter shade. Even less appreciated in Spain, its cultivation is devoted almost entirely to European export. It is more typical of winter, less watery, and sweeter.
Basque or Mallorca. Although it can be much larger, it is reminiscent of the peanut for its shape with a very elongated body. The skin is dark green with elongated lighter stripes, which can color the skin in yellowish tones. The pulp of intense orange color was darker than the peanut.Common pumpkins
Cucurbita maxima. We could say that it is the classic Halloween pumpkin, the most iconic that everyone visualizes when thinking about this vegetable. Rounded, flat, of variable size that can reach enormous dimensions, with somewhat rough and problematic skin, crossed by more or less deep furrows from the upper end to the base.
Sweet baked pumpkin. It is more rustic in appearance than the previous one but with a similar shape, although it can grow more cylindrical and elongated and not so rounded. The skin is thick, rough, and challenging, typical of winter, with long conservation and multiple culinary uses.
Totara pumpkin. It is very typical in the Region of Murcia and nearby areas; it has a similar shape to the previous one but is clearly distinguished by its thick dark green skin, full of warts or irregular bulbs. The inner meat can have an intense orange or more yellowish color, and it is highly appreciated in stews and stews. It can reach a large size, always rounded and flattened.
Gray pumpkin. Similar to the Costanera but with a smooth skin, divided into more pronounced segments by the furrows that run from one end to the other. It is distinguished by that more homogeneous, delicate skin and the dull, grayish ocher color. The pulp is firm and dense, dark orange or somewhat yellowish.















Add Comment